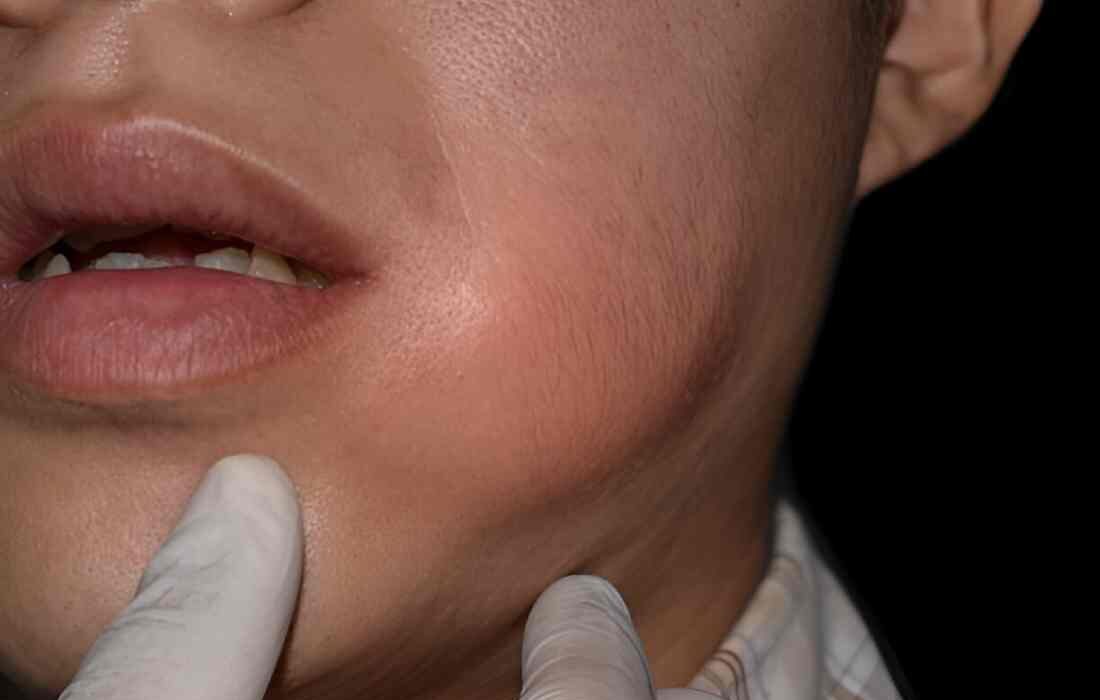
Gum boils, also known as dental abscesses or parulis, are a common dental issue that can cause discomfort and indicate underlying oral health problems. These boils appear as small, pimple-like swellings on the gums and are often filled with pus. They are typically a sign of infection in the tooth caused by the surrounding gum tissue. In this artifact, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gum boils, accompanied by a visual representation to help you identify them.
What Do Gum Boils Look Like?
Gum boils are usually small, round, and swollen bumps on the gums. They can vary in size and color, often appearing red or white due to pus. The surrounding area may be inflamed, and the boil can be tender to the touch. Sometimes, the boil may rupture, releasing pus and temporarily relieving pain. Below is a description of a typical gum boil image:
Location: Gum boils are commonly found near the base of a tooth, particularly in areas with decay or infection.
Appearance: The boil may look like a pimple or blister with a whitish or yellowish center.
Surrounding Tissue: The gums around the boil may appear red, swollen, and irritated.
Causes of Gum Boils
Bacterial infections primarily cause gum boils. The most common causes include:
Tooth Decay: Untreated cavities jerry can lead to infections in the tooth pulp, which may spread to the gums and form a boil.
Gum Disease: Periodontal sicknesses, such as gingivitis or periodontitis, can cause infections that result in gum boils.
Dental Trauma: Wounds to the teeth or gums can create beginnings for bacteria to enter and cause infections.
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate scrubbing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, increasing the risk of infections.
Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to oral infections.
Symptoms Associated with Gum Boils
In addition to the visible swelling, gum boils may cause the following symptoms:
- Pain or Discomfort: The exaggerated area may be tender, especially when chewing or applying pressure.
- Bad Breath: The infection can produce a foul odor.
- Pus Drainage: If the boil ruptures, pus may be released, sometimes accompanied by a metallic taste.
- Swelling: The gums and surrounding facial area may become swollen.
- Fever: The infection can lead to fever and general malaise in severe bags.
Treatment Options for Gum Boils
If you suspect you have a gum boil, it is essential to seek professional dental care. Treatment options may include:
- Drainage: A dentist may drain the boil to remove pus and relieve pressure.
- Antibiotics: If the infection is severe, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the bacteria.
- Root Canal Therapy: If the infection originates from the tooth pulp, a root canal may be necessary to save the tooth.
- Tooth Extraction: In cases where the tooth cannot be saved, extraction may be required.
- Improved Oral Hygiene: Maintaining proper oral care can prevent future infections.
Preventing Gum Boils
Prevention is key to avoiding gum boils. Here are some tips to keep your gums healthy:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth.
- Visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings.
- Avoid sugary foods and drinks that can contribute to tooth decay.
- Address dental issues, such as cavities or gum disease, promptly.
Conclusion
Gum boils are a clear sign of infection and should not be ignored. By understanding their appearance, causes, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to keep your health. If you notice a gum boil or experience related symptoms, consult your dentist immediately to prevent complications. Remember, early intervention is crucial for effective treatment and recovery.